 中文版
中文版



Welcome to contact us by phone:0086-0312-7969888
The internal structure of a stage electric motor can vary depending on the specific type and design of the motor. However, I can provide a general overview of the components commonly found in an electric motor used for stage applications:
Stator:
The stator is the stationary part of the motor and typically consists of a core made of laminated iron sheets. It contains coils of wire that are connected to the power supply.
Rotor:
The rotor is the rotating part of the motor. It is usually mounted on a shaft and is positioned within the stator. The rotor can be made up of conductive windings or permanent magnets.
Windings:
In motors with wound rotors or stators, coils of wire, known as windings, are used to create electromagnetic fields. The windings are connected to the power supply.
Permanent Magnets (if applicable):
In motors with permanent magnet rotors, permanent magnets are used to generate the magnetic field. These magnets are typically made of materials like neodymium or ferrite.
Bearings:
Bearings support the rotating shaft, allowing it to turn smoothly. Bearings are crucial for reducing friction and ensuring the longevity of the motor.
Shaft:
The shaft is a central component that connects the rotor to the external load, allowing the rotational motion of the motor to be transferred to the equipment it is driving.
Housing or Frame:
The housing or frame encases the motor's internal components, providing protection and structural support. It also serves as a mounting structure for the motor.
Cooling System (if applicable):
Larger motors or those used in applications with high operational demands may have a cooling system, such as a fan or cooling fins, to dissipate heat generated during operation.
Encoder or Sensor (if applicable):
Some stage motors may be equipped with encoders or sensors to provide feedback on the motor's position, speed, or other parameters. This feedback is used for precise control and positioning.
Control Electronics:
The control electronics include components like the motor controller and associated circuitry. These electronics manage the power supply to the motor, allowing for controlled and variable-speed operation.
Power Supply Connectors:
The motor has connectors for power supply input. The electrical connections enable the motor to be connected to an external power source.
It's important to note that the specific design and features of stage electric motors can vary based on factors such as motor type (AC or DC), size, power rating, and the application for which they are intended. For detailed information about a particular motor, it's recommended to refer to the manufacturer's documentation or specifications.

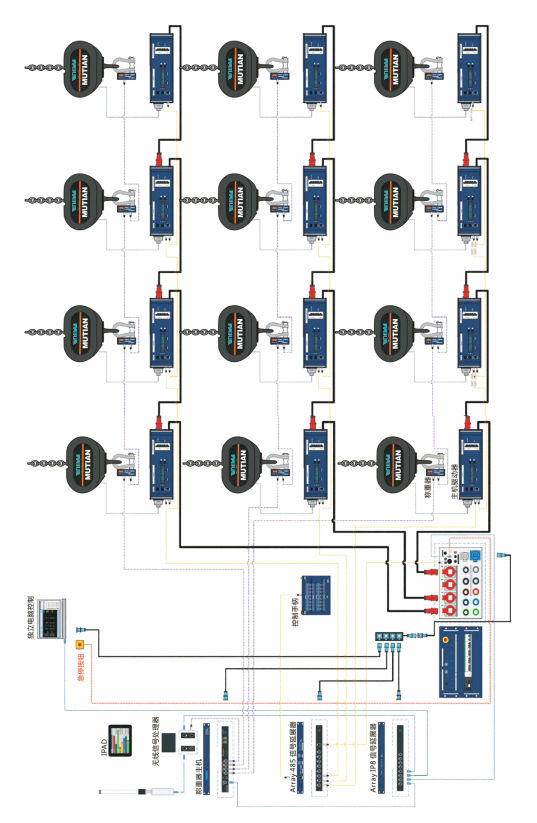




X