 中文版
中文版


Welcome to contact us by phone:0086-0312-7969888
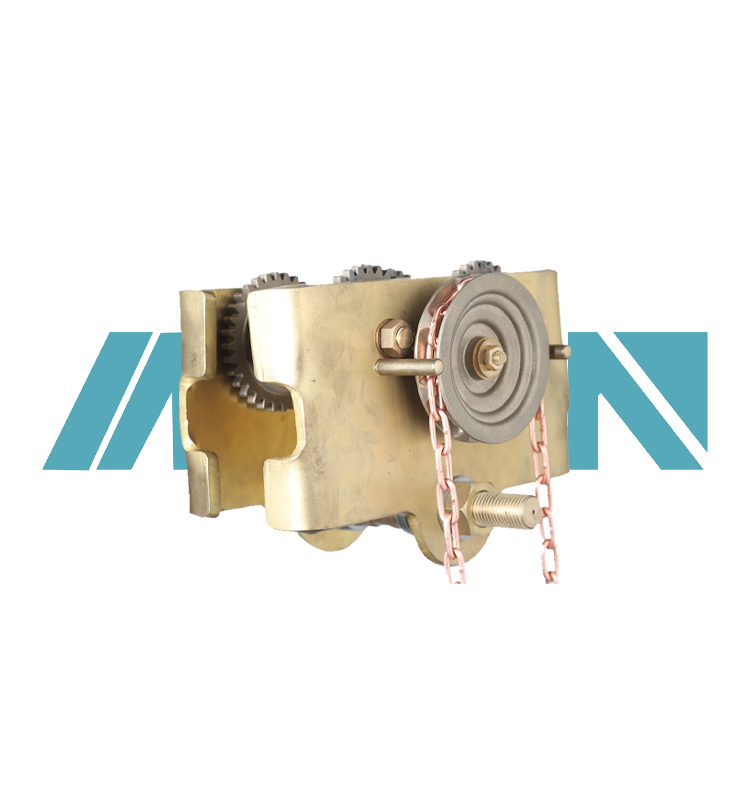
The overall material used for an explosion-proof chain hoist trolley is selected to ensure both strength and resistance to the potential hazards of an explosive environment. Here are some of the key materials typically used in the construction of an explosion-proof chain hoist trolley:
Explosion-proof Steel: Steel is a common material for the structural components of the trolley, such as the frame and support brackets. However, in explosion-proof applications, special alloys or treatments may be applied to the steel to enhance its resistance to sparks, heat, and flame.
Non-sparking Materials: Components that are in direct contact with explosive atmospheres, such as chain guides, hooks, and other fittings, are often made from non-sparking materials. These include copper, bronze, aluminum, or other alloys that are non-ferrous and do not generate sparks when in contact with each other or other surfaces.
Flame-resistant Plastics: Plastics and polymers may be used for non-structural parts of the trolley, such as handles, guards, or enclosures. These materials are selected for their flame resistance and ability to withstand high temperatures without igniting.
Explosion-proof Coatings: Some components may be coated with special paints or finishes that provide additional protection against sparks and ignition. These coatings can help enhance the explosion-proof characteristics of the trolley.
Explosion-proof Components: Components such as bearings, motors, and electrical systems are specifically selected for their explosion-proof ratings. These components are designed to prevent the generation of sparks or heat that could ignite explosive atmospheres.
It's important to note that the specific materials used for an explosion-proof chain hoist trolley will depend on the specific requirements and standards set by the applicable regulations and industry standards. Manufacturers of explosion-proof equipment are required to comply with these standards to ensure the safety of their products in explosive environments.
X